Canadian Substance Use Costs and Harms Online Data Visualisation Tool
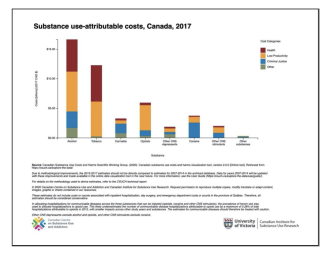
CSUCH’s data visualisation tool can be used to estimate substance use trends across the country. The data helps inform programs, practices, and research to protect communities, save lives, and improve the well-being of people in Canada.
Spotlight: Top 3 causes of death due to substance use in Canada
More than 200 people died each day due to substance use (SU) in 2020 (the latest year for which data are available). That works out to 73,994 deaths that year. The average age of death due to SU was 45 years. Tobacco use caused 63% (46,366) of SU-related deaths, followed by alcohol at 23%...